1) moment invariants


矩不变
1.
The authors have studied the moment invariants theory of pattern recognition,and combined the other image processing techniques,then developed a bar code identification system which can recognize not only the lightly polluted and incomplete bar code but also the distorted bar code with arbitrarily angle.
以矩不变为特征的模式识别理论为依据 ,结合其他数字图像处理技术 ,开发出不仅能对有轻度污染与残缺的条码进行识读 ,而且能对有任意角度畸变的条码图像进行快速识别的系统 ,从而扩大了条码的应用领
2) invariable intensity moment


矩不变
1.
The intensity moment of images and the method used for the bi-level threshold of images with invariable intensity moment are introduced.
介绍了图像的矩以及在保持图像的矩不变的条件下对图像进行两级阈值分割的方法,但该算法具有一定的盲目性,分割出来的图像具有过多的无用背景信息。
3) invariant moment


不变矩
1.
Recognition for sonar image based on improved histogram invariant moments;


基于改进直方图不变矩的声呐图像识别方法
2.
Target s matching method for the remote sensing image based on the histogram invariant moments;
基于直方图不变矩的遥感影像目标匹配方法
3.
Application of ART-2 neural network and invariant moment in image pattern recognition;


基于ART-2神经网络及不变矩特征的图像模式识别
4) Moment Invariants


不变矩
1.
Recognition of airfields in forward looking infrared image sequences by affine moment invariants;
基于不变矩的前视红外图像机场目标识别
2.
The application of moment invariants in checking the drug s packaging quality;


不变矩在药品包装质量检测中的应用
3.
Recognition of infrared image in sea level by moment invariants;


基于不变矩的海面红外目标识别
5) invariant moments


不变矩
1.
Recognition of ship by support vector machine and Invariant Moments;


基于不变矩和支持向量机理论的船舰目标识别
2.
Checking consistency between drawings based on image invariant moments in wavelet domain;


基于小波域图像不变矩的图纸一致性检测
3.
Application of a new invariant moments on image recognition;


一种新型不变矩在图像识别中的应用
6) Moment invariants


矩不变量
1.
Analysis of the invariance of moment invariants under discrete condition;


离散条件下数字图像矩不变量不变性的分析与研究
2.
Application of Curved Surface Moment Invariants


曲面轮廓矩不变量及其应用
3.
Regarding the phase function as model function,new moment invariants were generated.


为了克服矩不变量存在的高阶矩计算不稳定和对噪声敏感的问题,提出一种构造相位矩不变量的方法。
补充资料:传动:液力变矩器
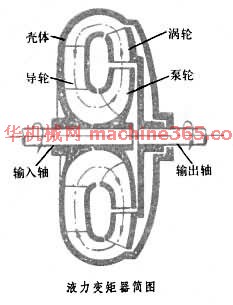
以液体为工作介质的一种非刚性扭矩变换器﹐是液力传动的型式之一。图 液力变矩器简图 为液力变矩器﹐它有一个密闭工作腔﹐液体在腔内循环流动﹐其中泵轮﹑涡轮和导轮分别与输入轴﹑输出轴和壳体相联。动力机(内燃机﹑电动机等)带动输入轴旋转时﹐液体从离心式泵轮流出﹐顺次经过涡轮﹑导轮再返回泵轮﹐周而復始地循环流动。泵轮将输入轴的机械能传递给液体。高速液体推动涡轮旋转﹐将能量传给输出轴。液力变矩器靠液体与叶片相互作用產生动量矩的变化来传递扭矩。液力变矩器不同於液力耦合器的主要特徵是它具有固定的导轮。导轮对液体的导流作用使液力变矩器的输出扭矩可高於或低於输入扭矩﹐因而称为变矩器。输出扭矩与输入扭矩的比值称变矩係数﹐输出转速为零时的零速变矩係数通常约2~6。变矩係数随输出转速的上昇而下降。液力变矩器的输入轴与输出轴间靠液体联繫﹐工作构件间没有刚性联接。液力变矩器的特点是﹕能消除衝击和振动﹐过载保护性能和起动性能好﹔输出轴的转速可大於或小於输入轴的转速﹐两轴的转速差随传递扭矩的大小而不同﹔有良好的自动变速性能﹐载荷增大时输出转速自动下降﹐反之自动上昇﹔保证动力机有稳定的工作区﹐载荷的瞬态变化基本不会反映到动力机上。液力变矩器在额定工况附近效率较高﹐最高效率为85~92%。叶轮是液力变矩器的核心。它的型式和布置位置以及叶片的形状﹐对变矩器的性能有决定作用。有的液力变矩器有两个以上的涡轮﹑导轮或泵轮﹐藉以获得不同的性能。最常见的是正转(输出轴和输入轴转向一致)﹑单级(只有一个涡轮)液力变矩器。兼有变矩器和耦合器性能特点的称为综合式液力变矩器﹐例如导轮可以固定﹑也可以随泵轮一起转动的液力变矩器。为使液力变矩器正常工作﹐避免產生气蚀和保证散热﹐需要有一定供油压力的辅助供油系统和冷却系统。
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条