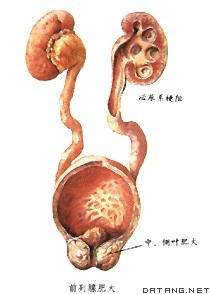
1) Benign prostatic hyperplasic model rats


前列腺增生模型鼠
3) prostate cancer mouse model


前列腺癌小鼠模型
1.
Considering the reasons mentioned above, the concerned study was carried out based on the following components: (1) Microarray used to screen the differential highly expressed genes with unknown function in prostate between wild type mice and KIMAP prostate cancer mouse model (by 20th week and 60th week).
利用前列腺分泌蛋白94(PSP94)启动子建立的基因敲入前列腺癌小鼠模型(KIMAP),显示与人类相近的肿瘤特征。
4) prostatic hyperplasia


前列腺增生
1.
Transurethral plasmakinetic resection of prostate for treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia;
经尿道等离子体双极电切术治疗前列腺增生
2.
Transurethral electro resection for prostatic hyperplasia with small volume:A report 30 cases;
经尿道电切治疗小体积前列腺增生30例
3.
A comparative study and evaluations on the results of TURP and transrectal high intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia;
经直肠高能聚焦超声与经尿道前列腺切除术治疗前列腺增生症近期疗效比较
5) Prostate hyperplasia


前列腺增生
1.
The significance of fibroblast growth factor 7 mRNA expression in benign prostate hyperplasia tissue;
成纤维细胞生长因子-7在前列腺增生组织中的表达
2.
Expression effect study of Xianjia prescription on prostate s bcl-2 and bax in benign prostate hyperplasia rats;
仙甲汤对前列腺增生大鼠前列腺组织bcl-2及bax表达影响的研究
3.
Detection of serum prostate specific antigen in cases of prostate hyperplasia;


前列腺增生患者前列腺特异性抗原测定
6) Benign prostatic hyperplasia


前列腺增生
1.
Treatment of senior and high risk benign prostatic hyperplasia by transurethral electrovaporization and resection of prostate;
高龄高危前列腺增生经尿道电汽化联合电切的临床探讨
2.
Effect of Xianjia prescription on the expression of FAS in rats prostate exponent of benign prostatic hyperplasia;
仙甲汤对实验性前列腺增生大鼠前列腺组织FAS蛋白表达的影响
3.
Transurethral electrovaporization of prostate for treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia and management of its complications(a report of 612 cases);
经尿道前列腺电汽化术治疗良性前列腺增生及并发症的防治(附612例报告)
补充资料:前列腺增生
| 前列腺增生 prostate,hyperplasia of 老年男性常见疾病 。又称良性前列腺增生、前列腺肥大。严格讲老年人发生的是前列腺增生而不是肥大。病变表现为细胞增多即增生,不是细胞肥大。但因名称沿用多年,临床上多通用。国内外尸检都表明,60岁以上男性半数以上可以发现前列腺组织学增生,但1/4为肉眼可见的增大前列腺,其中一半可能需要治疗。前列腺增生发生的机制尚不完全清楚。 临床表现主要为排尿异常。症状可分为梗阻和刺激两类;梗阻症状为排尿踌躇、间断、终末滴沥、尿线细而无力、排尿不尽等。刺激症状为尿频、夜尿多、尿急、尿痛。症状可因寒冷、饮酒及应用抗胆碱药、精神病药物等加重。长期梗阻可导致乏力、嗜睡、恶心呕吐等尿毒症症状。 直肠指诊可发现前列腺增大,中间沟消失或隆起,应注意有无坚硬结节,是否存在前列腺癌。B超可检查前列腺大小、结构是否异常及膀胱有无残余尿等。CT 及MRI有助于鉴别前列腺癌。尿流率检查可了解排尿梗阻程度。还应与尿道狭窄、神经性膀胱功能障碍鉴别,神经病变在直肠指诊时肛门括约肌松弛,并有其他神经病变症状。
前列腺增生的体积大小与临床症状并不平行,症状亦可时轻时重,治疗决定于症状轻重和是否存在并发症。药物治疗主要用于症状轻无并发症者。常用的药物有:①a 阻滞剂。如酚苄明,容易有低血压 、头晕等副作用。近年采用a1阻滞剂,如高特灵等,副作用少。②5a还原酶抑制剂。减少双氢睾酮形成。③降低胆固醇药物。如甲帕霉素等。④植物药。⑤其他。如黄酮哌酯等亦可减轻症状。此外,微波、射频、激光治疗,气囊扩张,前列腺尿道支架等亦可用于治疗。手术是主要治疗方法。经尿道前列腺切除术,术后恢复快,但需有特殊设备和技术。开放手术适用于并发结石、前列腺增生体积大的病例。手术主要是切除围绕尿道的前列腺增生部分即移行带。由于容易发生癌的外围带常被压扁,和增生部分有清楚界限,手术时保留,因此术后仍有可能发生前列腺癌。 |
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条