1) serious autoimmune disease


重症自身免疫性疾病
1.
Treatment for serious autoimmune disease with plasma exchange therapy after suboptimal response to large doses of steroids;
血浆置换术治疗大剂量激素及免疫抑制剂疗效不佳的重症自身免疫性疾病
2) refractory severe autoimmune disease


难治性重症自身免疫病
1.
Objective To investigate the clinical effect of Chinese herbal medicine combined with auto-hemo- poietic stem cell transplantation for refractory severe autoimmune disease(RSAID).
目的探讨中药联合造血干细胞移植治疗难治性重症自身免疫病的临床疗效。
3) autoimmune disease


自身免疫性疾病
1.
Application of proteomics in autoimmune diseases;


蛋白质组学在自身免疫性疾病中的应用
2.
Epidemiological and clinical manifestation of human parvovirus B19 infection in children with autoimmune diseases;
儿童自身免疫性疾病人细小病毒B19感染及其临床特征
3.
Autoimmune diseases complicated by malignancy: a case report of 17 patients.;


自身免疫性疾病合并恶性肿瘤17例分析
4) autoimmune diseases


自身免疫性疾病
1.
DNA methylation and autoimmune diseases;


DNA甲基化与自身免疫性疾病
2.
Relationship between IL-17 and autoimmune diseases;


IL-17与自身免疫性疾病关系的研究进展
3.
Estrogen in autoimmune diseases;


雌激素与自身免疫性疾病
5) autoimmune thyroid disease


自身免疫性甲状腺疾病
1.
Expression of CCR5 and CD30 molecules in peripheral blood lymphocytes of patients with autoimmune thyroid disease;
CCR5和CD30在自身免疫性甲状腺疾病外周淋巴细胞上的表达
2.
Th1/ Th2 cells polarization in children with autoimmune thyroid diseases


儿童自身免疫性甲状腺疾病Th1/Th2细胞极化偏移的研究
3.
Value of four urinary trace proteins in the diagnosis of early renal impairment caused by autoimmune thyroid disease
4种尿微量蛋白在儿童自身免疫性甲状腺疾病早期肾损害诊断中的意义
6) AITD


自身免疫性甲状腺疾病
1.
Different sensitivity of thyroid cells of normal and AITD patients to iodide on inducing antigen expression;
正常人和自身免疫性甲状腺疾病患者甲状腺细胞对碘致抗原表达的不同敏感性
2.
AIM: To identify the presence of previously reported thyroglobulin (Tg) gene single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) in Chinese people and to investigate their potential relation to the aetiology of autoimmune thyroid disease (AITD).
目的检测中国人甲状腺球蛋白(Tg)基因的外显子10,12,33是否存在单核苷酸多态性(SNP),研究其与自身免疫性甲状腺疾病(AITD)的关系。
3.
The expression of the apoptosis-related protein Fas and FasL in the thyroid epithelial cells(TEC) from patients with autoimmune thyroid disease(AITD) was measured, to investigate the role of apoptosis in AITD pathogenesis.
测定凋亡相关蛋白Fas、FasL在自身免疫性甲状腺疾病 (AITD)病人甲状腺细胞中的表达 ,以研究细胞凋亡在AITD发病中的作用。
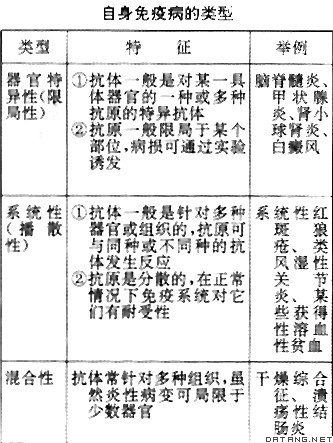
补充资料:自身免疫性疾病
| 自身免疫性疾病 autoimmune diseases 自身免疫反应达到一定程度而导致的疾病。免疫系统最基本的功能是认识自身和识别异体,达到保护自身和排斥异体的目的。正常人体血清中可存在多种针对自身抗原的抗体,但它们的水平极低,不足以破坏自身成分,可清除衰老退变的自身组织,这就是自身免疫反应。当这种反应过强,导致严重组织损伤,表现出临床症状时,就称为自身免疫病。 自身免疫过程通常通过盖尔及库姆斯二氏分型的Ⅲ型变态反应导致组织损伤。自身组织(自身抗原)先刺激免疫系统导致自身抗体产生,此两者结合成免疫复合物,再引起组织损伤。自身免疫也可通过Ⅳ型变态反应机理,直接因淋巴细胞的激活而发生。关于自身免疫过程发生的机理,有多种学说: ①禁忌细胞系学说。身体中出现突变淋巴细胞,并由于某种刺激而增殖活跃起来。由于这种突变淋巴细胞系抗原结构上的异常,使它将正常的自身组织认为异体,发生免疫反应而导致组织损伤。 ②隐蔽抗原学说。在胚胎的发育过程中,只有曾受淋巴网状系统检验的组织才被识别为自身组织,受到保护。有些器官和组织,例如中枢神经系统、甲状腺、晶体、精子等,在胚胎期没有被免疫系统识别,因此不受保护,一旦因为感染、外伤等原因,这些组织的自身抗原释放入血液或淋巴液,就可刺激产生自身抗体,造成组织损伤。 ③自身变异学说。正常组织受物理、化学或生物性刺激而发生变异,被免疫系统识别为非自身组织而受到排斥。 ④免疫清除功能障碍学说。由于免疫缺陷,不能有效地清除突变的淋巴细胞或抗原,导致自身免疫过程。 ⑤交叉反应抗体学说。由于机体的某些组织成分与外界抗原具有相似的抗原性,当机体清除外界抗原时,同时损伤了这些具有相似抗原性的自身组织。 此外,自身免疫病的发生还与年龄、性别、遗传等多种因素有关,所以其机理可能是多方面的。 自身免疫病有多种类型。由于发病机理不清楚,诊断、防治都比较困难,需要结合多方面的资料综合考虑。
自身免疫性疾病的治疗可归纳为以下4方面:①应用细胞毒制剂以破坏迅速增生的细胞系。②应用皮质类固醇以抑制自身免疫过程产生的病理刺激。③应用药物以拮抗自身免疫过程中释放出的药理活性物质的作用和造成的损害。④如果有可能除去产生自身抗原的病灶,则手术也可作为治疗自身免疫病的一个手段。 |
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条