1) visceral hyperalgesia


内脏痛觉过敏
1.
Objective To evaluate the role of vanilloid receptor 1 in visceral hyperalgesia in adult rats induced by colon irritation during postnatal development.
目的研究辣椒素受体(VR1)在肠易激综合征(IBS)内脏痛觉过敏中的作用。
2.
Objective: By giving mechanical and chemical stimuli to adult rats, our aim was to investiqate the mechanism of visceral hyperalgesia.
目的 :通过对成年大鼠给予机械和化学伤害性刺激 ,探讨内脏痛觉过敏产生的机制。
3.
Conclusion Antagonists of vanilloid receptor are effective to attenuate visceral hyperalgesia induced by water-avoid stress, and vanilloid receptor mediates process of visceral hyperalgesia.
目的研究避水应激引起内脏痛觉敏感性的变化及特异性辣椒素受体(VR1)拮抗剂辣椒平与非特异性VR1拮抗剂钌红对避水应激引起内脏痛觉过敏的治疗作用。
3) Visceral hypersensitivity


内脏感觉过敏
1.
Currently, the descending modulation and accending arousal mechanisms are considered to be the causes or risk factors contributing to the visceral hypersensitivity in IBS.
内脏感觉过敏被认为是IBS腹部疼痛或不适的主要机制。
4) hyperalgesia
[英][,haipəræl'dʒi:ziə] [美][,haɪpəræl'dʒizɪə]


痛觉过敏
1.
Relationship between Abnormal spinal complement activity and hyperalgesia in rats following sciatic nerve ligation;
坐骨神经结扎大鼠脑脊液补体异常活化与痛觉过敏的关系
2.
Intrathecal minocycline attenuates thermal hyperalgesia in a rat model of CFA-induced arthritis;
鞘内注射米诺环素减轻大鼠佐剂性关节炎性痛觉过敏
3.
Effects of NMDA receptors on hyperalgesia;


NMDA受体在痛觉过敏中的作用
6) thermal hyperalgesia


热痛觉过敏
1.
Peritoneal injection of botulinum toxin type A inhibited the development of mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia in a rat model of neuropathic pain;
腹腔注射肉毒毒素A抑制CCI模型大鼠机械性触诱发痛和热痛觉过敏的形成
2.
Effects of Clonidine on Capsaicin-induced thermal hyperalgesia;


可乐定对辣椒素热痛觉过敏的影响
3.
Objective To evaluate the role of protein kinase C(PKC) in the thermal hyperalgesia evoked by local injection of endothelin-1(ET-1).
目的研究蛋白激酶C(PKC)途径在内皮素-1(ET-1)引起热痛觉过敏中的作用。
补充资料:感觉传导途径 3痛觉、温度觉传入途径示意图
李瑞端绘
[图]
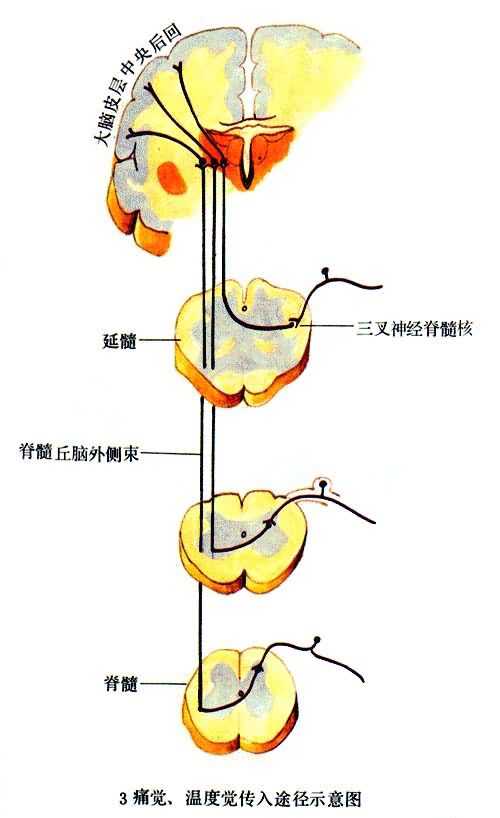
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条