1) Olfactory Receptor Neurons


嗅觉受体神经元
2) olfactory receptor neurons


嗅觉神经元
1.
Purpose To study whether apoptosis play a role in controlling the number of olfactory receptor neurons, so as to reveal the speciality and its relationship in neurogenesis.
目的 研究凋亡是否参与嗅上皮正常生理更替和嗅球摘除后嗅觉神经元死亡后再生过程 ,探讨凋亡与神经元再生的关系。
2.
Olfactory receptor neurons (ORNs) not only can regenerate,but also they are true bipolar neurons directly exposed to the external environment.
正常情况下,生物体内嗅觉神经元(olfactory receptor neurons, ORNs)的再生与凋亡处于动态平衡之中,即通过基底细胞生成,神经细胞分化、成熟,ORNs凋亡的动态平衡而维持正常的嗅觉功能。
4) Olfactory receptor


嗅觉受体
1.
Olfactory receptor(OR),as a kind of G protein-coupled receptors,is a key component of the olfactory system.
嗅觉受体(olfactory receptors,Ors)是G蛋白偶联受体(Gprotein-coupled receptor)的一种,是嗅觉系统的关键成分。
2.
Since the olfactory receptor genes identified in 1991,great achievements have been obtained on the molecular and cellular olfaction mechanism of insect.
自1991年在动物中发现嗅觉受体基因以来,关于昆虫感受化学信息的周缘神经系统的分子和细胞机制方面的进展十分迅速。
6) Olfactory receptor neurons ( ORNs )


嗅神经元
1.
Olfactory receptor neurons ( ORNs ) is a kind of special neuron in vertebrates.


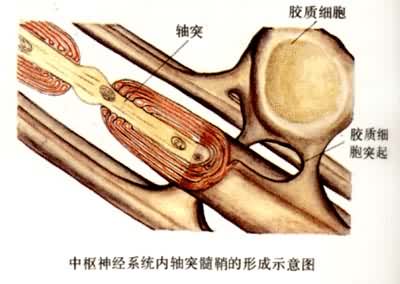
嗅神经元是脊椎动物的一类特殊的神经元,它的特殊性体现在:在初级感觉神经元中,嗅神经元是唯一胞体同外周环境相接触的神经元;嗅神经元的轴突没有被髓鞘化,在胚胎发育期,感觉神经元的轴突可形成神经束,并被雪旺细胞包裹,成体后这些神经束结构消失,代之以彼此分开并髓鞘化的轴突结构,但成体动物的嗅神经元依然保持这种胚胎期神经束的结构,其神经束被嗅鞘细胞松散包裹;不同于其他感觉系统,嗅觉信息可直接向皮层传递而不需要经过丘脑;嗅神经元最大的特殊性在于嗅神经元是脊椎动物唯一一种可终生不断再生的神经元,嗅神经元的再生是由位于嗅上皮基底层的干细胞完成的。
补充资料:神经元形态中枢神经系统内轴突髓鞘的形成示意图
李瑞端绘
[图]
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条