1) Hematuria
[英][,hi:mə'tju:riə] [美][,himə'tjurɪə]


血尿
1.
Clinical and pathological characteristics of patients with asymptomatic glomerular hematuria and risk factors asso-ciated with renal lesions;
无症状肾小球性血尿患者临床病理特点及其危险因素
2.
The phase contrast microscope and the UF 150 urines slime analyzer originates in the distinction at the hematuria the comparison;
相差显微镜与UF一50尿沉渣分析仪在血尿来源鉴别中的比较
3.
Hepatic injury and hematuria resulting from tranilast;


曲尼司特致肝损害和血尿
2) haematuria
[,hi:mə'tjuəriə]


血尿
1.
Objective To observe the clinical efficacy of "Ertong Xueniao Decoction" in the treatment of nutcracker haematuria.
目的观察儿童血尿方治疗儿童胡桃夹性血尿的临床疗效。
2.
Method During the course of clinical teaching, clinical teaching ability was improved by the heuristic method, through analysis of pathogeny of haematuria.
方法在临床教学中,通过启发式教学,从血尿病因分析出发培养实习医师正确的临床思维能力。
3) blood urine


血尿
1.
It narrated the complications of patients with detaining double-J-tube including aversion and regurgitation of stent tube,infection,irritative symptoms of bladder,formation of scaling and calculus,blood urine,ineffective drainage of double-J-tube and overtime detaining of double-J-tube.
叙述了留置双J管的并发症有支架管移位、反流、感染、膀胱刺激征、结垢与结石形成、血尿、双J管引流无效、双J过期留置,分析了发生并发症的原因,并对其进行针对性护理。
2.
Objective Reviewing and analysing the clinical process of the patient’s blood urine caused by Cefradine, and also studying the etiology of this phenomena.
目的回顾总结分析头孢拉定致患儿血尿的临床过程,并探讨其病因。
4) Blood/Urine


血/尿
5) urethral hematuria


尿道性血尿
6) Serum uric acid


血尿酸
1.
Relationship between lipid metabolism,related indexes of body fat and obesity,serum uric acid;
脂代谢相关指标和肥胖与血尿酸关系
2.
Correlation study of level of serum uric acid and change of blood coagulation and flbrinolysis in coronary heart disease patients;
冠心病患者血尿酸水平、凝血纤溶功能及其相关性研究
3.
Clinical observation of the serum uric acid level in the elderly with hypertension complicated with diabetes;
老年高血压合并糖尿病患者血尿酸水平的临床观察
补充资料:血尿
| 血尿 hematuria 含有红细胞的尿。血液经损伤的肾小球、肾小管或尿路混入尿中所致。由于血量不同分为镜下血尿和肉眼血尿。镜下血尿是眼睛看不见的血尿,需用显微镜观察。取离心尿沉渣观察,因血尿程度不同而分为 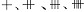 ,分别相当于每高倍视野有红细胞2~5个、6~20个、21~50个及51~100个。肉眼血尿是每升尿中血量超过1毫升,肉眼可见。引起血尿的原因很多,约98%的病因是泌尿系本身疾病所致,仅2%是由全身及泌尿系邻近器官疾病所致,如结肠、阑尾、盆腔的炎症或肿瘤,及某些血液病和心血管病。用相差显微镜观察尿红细 胞形态分为:① 肾小球源性血尿。红细胞大小不等,外形多样化,提示为肾小球病变引起 ,见于IgA及非IgA系膜增殖性肾炎 、薄基底膜肾病、遗传性肾炎、局灶性肾炎及过敏性紫癜、狼疮性肾炎等。血尿可为持续性,也可为发作性,且常伴蛋白尿。②外科性血尿。红细胞大小相等、圆形,见于泌尿系结石、肿瘤、炎症及前列腺肥大、肾下垂、肾血管异常。 ,分别相当于每高倍视野有红细胞2~5个、6~20个、21~50个及51~100个。肉眼血尿是每升尿中血量超过1毫升,肉眼可见。引起血尿的原因很多,约98%的病因是泌尿系本身疾病所致,仅2%是由全身及泌尿系邻近器官疾病所致,如结肠、阑尾、盆腔的炎症或肿瘤,及某些血液病和心血管病。用相差显微镜观察尿红细 胞形态分为:① 肾小球源性血尿。红细胞大小不等,外形多样化,提示为肾小球病变引起 ,见于IgA及非IgA系膜增殖性肾炎 、薄基底膜肾病、遗传性肾炎、局灶性肾炎及过敏性紫癜、狼疮性肾炎等。血尿可为持续性,也可为发作性,且常伴蛋白尿。②外科性血尿。红细胞大小相等、圆形,见于泌尿系结石、肿瘤、炎症及前列腺肥大、肾下垂、肾血管异常。血尿出现在排尿之初称初血尿,见于尿道疾病;排尿终出现血尿称终末血尿,见于膀胱颈部、三角区及后尿道疾病;全排尿过程中均有血尿,提示血尿来自肾脏或膀胱的疾病。应排除由月经期或子宫阴道出血所致的血尿。 |
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条