1) Torque converter
变矩器
1.
A dynamic model for variable-speed torque converter with adjustable guide blades;
导叶可调式液力变矩器数学模型的建立
2.
The Application of Numerical Simulation on the Flow Field of Hydrodynamic Torque Converter;
数值模拟技术在液力变矩器流场分析中的应用
3.
The leakage, wear and high oil temperature faults of transmissions box and torque converters for loaders are analyzed.
分析了装载机变速箱、变矩器泄漏、磨损和油温过高的原因,介绍了其危害,并针对每一种故障均提出了相应的修复措施。
2) Converter
变矩器
1.
A Model of Automatic Identification and Optimization for Matching Generator with Torque Converter;
发动机与变矩器匹配的自动识别与优化模型
3) torque-converter
变矩器
1.
Reasons of high temperature of torque-converter for wheel loader;
轮式装载机变矩器温升过高的原因分析
2.
A dynamic mathematic model is presented in this paper for pump impeller rotational speed hydraulic torque-converter.
本文建立了变泵轮转速液力变矩器控制系统的动态数学模型,并对模型进行了仿真和试验验证。
4) hydraulic torque converter
液力变矩器
1.
Performance analysis of hydraulic torque converter drive pumping unit;
电动机加液力变矩器驱动抽油机的性能分析
2.
Design of Control System of new tractor-brake hydraulic torque converter;
新型牵引-制动型液力变矩器控制系统的开发设计
3.
Three-dimensional design for hydraulic torque converter blades and its performance analysis;
液力变矩器叶片三维成型法及其性能分析
5) torque converter
液力变矩器
1.
Calculation and analysis of internal characteristics of torque converter-coupling;
综合式液力变矩器内特性的计算与分析
2.
Characteristics prediction of a torque converter based on three dimensional numerical calculation of flow field;
基于三维流场计算的液力变矩器特性预测方法
3.
The optimum power gear-shifting regularity of automobile auto-transmission with torque converter;
装有液力变矩器的自动变速汽车的最佳动力性换档规律
6) hydrodynamic torque converter
液力变矩器
1.
Method of internal 3-D flow field numerical simulation for hydrodynamic torque converter;
液力变矩器内部三维流动计算方法
2.
Amendment to circulatory circle on hydrodynamic torque converter;
液力变矩器循环圆的修正
3.
The study on the constructing method of hydrodynamic torque converter surface;
液力变矩器的准确三维造型方法研究
参考词条
柴油机变矩器组
液力机械变矩器
变量式变矩器
单级液力变矩器
液力偶合器与变矩器
变矩器-变速箱系统
可调式液力变矩器
闭锁式液力变矩器
导叶可调式液力变矩器
液力变矩器上盖与连接块
液力变扭器/闭锁式变矩器
发动机与液力变矩器的共同工作特性
评价实例
自动配页机
补充资料:传动:液力变矩器
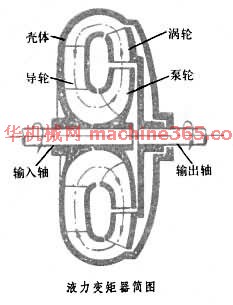
以液体为工作介质的一种非刚性扭矩变换器﹐是液力传动的型式之一。图 液力变矩器简图 为液力变矩器﹐它有一个密闭工作腔﹐液体在腔内循环流动﹐其中泵轮﹑涡轮和导轮分别与输入轴﹑输出轴和壳体相联。动力机(内燃机﹑电动机等)带动输入轴旋转时﹐液体从离心式泵轮流出﹐顺次经过涡轮﹑导轮再返回泵轮﹐周而復始地循环流动。泵轮将输入轴的机械能传递给液体。高速液体推动涡轮旋转﹐将能量传给输出轴。液力变矩器靠液体与叶片相互作用產生动量矩的变化来传递扭矩。液力变矩器不同於液力耦合器的主要特徵是它具有固定的导轮。导轮对液体的导流作用使液力变矩器的输出扭矩可高於或低於输入扭矩﹐因而称为变矩器。输出扭矩与输入扭矩的比值称变矩係数﹐输出转速为零时的零速变矩係数通常约2~6。变矩係数随输出转速的上昇而下降。液力变矩器的输入轴与输出轴间靠液体联繫﹐工作构件间没有刚性联接。液力变矩器的特点是﹕能消除衝击和振动﹐过载保护性能和起动性能好﹔输出轴的转速可大於或小於输入轴的转速﹐两轴的转速差随传递扭矩的大小而不同﹔有良好的自动变速性能﹐载荷增大时输出转速自动下降﹐反之自动上昇﹔保证动力机有稳定的工作区﹐载荷的瞬态变化基本不会反映到动力机上。液力变矩器在额定工况附近效率较高﹐最高效率为85~92%。叶轮是液力变矩器的核心。它的型式和布置位置以及叶片的形状﹐对变矩器的性能有决定作用。有的液力变矩器有两个以上的涡轮﹑导轮或泵轮﹐藉以获得不同的性能。最常见的是正转(输出轴和输入轴转向一致)﹑单级(只有一个涡轮)液力变矩器。兼有变矩器和耦合器性能特点的称为综合式液力变矩器﹐例如导轮可以固定﹑也可以随泵轮一起转动的液力变矩器。为使液力变矩器正常工作﹐避免產生气蚀和保证散热﹐需要有一定供油压力的辅助供油系统和冷却系统。
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。