1) Basal respiration


基础呼吸
1.
05),basal respiration and metabolic quotient qCO2 decreased(P<0.


05)、以及土壤微生物生物量碳,降低了土壤基础呼吸和代谢商(P<0。
2.
The results showed that cultivation resulted in decrease in the microbial biomass carbon(MBC),microbial quotient(MQ),and basal respiration(BR).
结果表明,沼泽湿地垦殖初期(1~3年),土壤微生物量碳(MBC)、微生物商以及基础呼吸(BR)都迅速降低,而代谢商(qCO2)、PR/BR和PR/MBC比值却不断升高。
2) root-free soil respiration


基础土壤呼吸
1.
A Free-Air Carbon Dioxide Enrichment (FACE) system and root-isolation methods were used to study the effects of elevated pCO2 on soil respiration, root-free soil respiration and theirs influencing factors, determined by in sit.
)轮作制中麦田的土壤呼吸、基础土壤呼吸和呼吸主要影响因子,分析了大气CO2体积分数升高后温度与水分对土壤呼吸的影响。
3) soil basal respiration


土壤基础呼吸
1.
00 mg·kg-1),but was inhibited consistently with increasing Cd concentrations;soil basal respiration was restrained at low Cd loading(<1.
00 mg·kg-1时,土壤微生物生物量碳增加,土壤基础呼吸作用略有减弱;随着外加镉浓度的增加,微生物生物量碳呈下降趋势,呼吸作用加强。
2.
However,soil microbial biomass C,N,and soil basal respiration all decreased with PCBs contents increasing in soils.
以多氯联苯(Polychlorinated biphenyls,PCBs)自然污染的农田土壤为材料,分析土壤中微生物区系组成、生物量C、N、土壤基础呼吸以及微生物群落功能多样性的变化。
4) soil basal respiration


土壤基础呼吸作用
1.
Different added lead concentration ranging from 200 mg/kg to 1 200 mg/kg effect on soil basal respiration,soil biomass carbon,metabolic quotient and dehydrogenase activity.
通过室内培养,研究了不同铅添加水平(200~1 200 mg/kg)对青紫泥田微生物生物量碳及土壤基础呼吸作用、土壤代谢商、土壤脱氢酶的影响。
5) Respiratory material


呼吸基质
6) substrate respiration


基质呼吸
补充资料:呼吸系统的进化鱼的呼吸器官及气体交换示意图
李瑞端绘
[图]
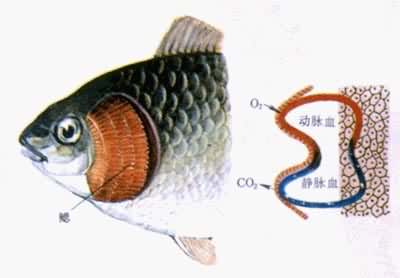
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条