1) Cenozoic
[英][,si:nə'zəuik] [美][,sinə'zoɪk]


新生代
1.
Features of Cenozoic Hydrocarbon Accumulation in Honggouzi Structure,Qaidam Basin;


柴达木盆地红沟子鼻状构造新生代油气成藏特征
2.
Cenozoic Wave Processes and Their Relationships to Hydrocarbon in the Qaidam Basin;


柴达木盆地新生代波动过程及与油气关系
3.
Cenozoic tectonic evolution and hydrocarbon accumulation in Bonan Region;


渤南地区新生代构造演化与油气成藏
2) Cenozoic era


新生代
1.
Tectonic uplift of the Cenozoic era in the Qinling Range;


秦岭新生代构造隆升研究
2.
The Transformation of the Cenozoic Era Movie s Esthetic Style;


论新生代电影的审美风格转变
3.
Lakes developed widely during Cenozoic era in central Tibetan Plateau.


青藏高原中部新生代湖泊发育普遍。
3) new generation


新生代
1.
Something on The Commercial Features of Works by “the New Generation”;


浅议“新生代”作品的商品化特征
2.
From "Fragment Snapshot" of "New Generation" to "Cruelty Youth" of "Later Generation";


从“新生代”的“片断快照”到“后生代”的“青春残酷”
3.
Due to the cross-generation difference,the writers of new generation have the difference with those in the new period in the aspects of experiencing it and historical memory while narrating the Great Cultural Revolution.
新生代作家和新时期之初"文革"叙事的作家由于其"代际差异",有着"文革"亲历和历史记忆之别。
4) the new generation


新生代
1.
The study shows:The Chinese movie′s narrative pattern is developing gradually after innovating "the film language′s mordernization" and "the new generation" on the basis of" concept of.
研究认为:中国电影的叙事模式是在"影戏观"的基础上,经过"电影语言的现代化"和"新生代"的革新,逐渐发展演变的。
2.
The author stemmed from the attention on peasant workers and chose the families of the new generation of peasant workers in Shanghai as the object of study.
笔者源于对农民工群体的关注,选择了以家庭流动方式来上海务工经商的新生代农民工家庭的消费结构为研究对象。
3.
The Chinese Western theme movie of the new generation refers to the films which the directors of the new generation produce and use the general western area as the story s background.
新生代西部题材电影是指中国新生代导演以广大的西部地区作为故事发生背景所拍摄的影片。
5) Meso-Cenozoic


中新生代
1.
Analysis of joints from the Meso-Cenozoic tectonic stress field in the west section of south Dabashan fault-fold belt in China;
南大巴山褶断带西段中新生代构造应力场的节理研究
2.
Meso-Cenozoic tectonic setting and evolution of East China Sea shelf basin;


东海陆架盆地中新生代构造背景及演化
3.
Structural deformation mechanism of the Meso-Cenozoic basementand cover in the north Tarim uplift-Kuqa depression;
塔北隆起—库车坳陷区中新生代基底-盖层构造变形机理
6) Mesozoic-Cenozoic


中新生代
1.
Discussion on Mesozoic-Cenozoic Evolution of Tian Shan and Its Adjacent Basins;


中新生代天山及其两侧盆地性质与演化
2.
Transition of the Mesozoic-Cenozoic Tectonic Regimes and Hydrocarbon Accumulation in Western Ordos Region;
鄂尔多斯西缘中新生代构造体制转换与油气聚集
3.
The Mesozoic-Cenozoic Extensional Tectonics in Western Shandong Province;


鲁西中新生代伸展构造研究
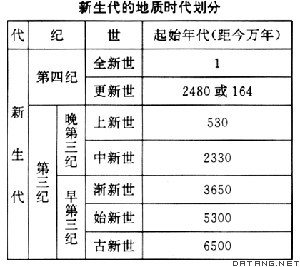
补充资料:新生代
| 新生代(距今6500万年~今) Cenozoic Era 地质历史上最新的一个代,显生宙的第三个代。这一时期形成的地层称新生界。新生代以哺乳动物和被子植物的高度繁盛为特征,由于生物界逐渐呈现了现代的面貌,故名新生代(即现代生物的时代)。1760年,意大利博物学家G.阿尔杜伊诺在研究意大利北部地质时,把组成山系的地层分为3个系:第一系为结晶岩,第二系为含化石的成层岩石,第三系为半胶结的层状岩石,常含海相贝壳。1829年,法国学者J.德努瓦耶研究巴黎盆地时,把第三系之上的松散沉积层称为第四系。第一系、第二系的名称已废弃不用,第一系大致相当前寒武系,第二系相当于古生代和中生代的地层。新生代包括第三纪和第四纪,第三纪又可分为早第三纪和晚第三纪,纪可再划分为几个世(见表)。 新生代开始时,中生代占统治地位的爬行动物大部分绝灭,繁盛的裸子植物迅速衰退,为哺乳动物大发展和被子植物的极度繁盛所取代。因此,新生代称为哺乳动物时代或被子植物时代。哺乳动物的进一步演化,适应于各种生态环境,分化为许多门类。到第三纪后期出现了最高等动物——原始人类。原始人类起源于亚洲或非洲。
新生代开始时,古地中海比现代大,欧亚大陆比现代小;中国和印度被古地中海隔开,土耳其和古波斯为古地中海的岛屿;红海尚未形成,阿拉伯半岛为非洲的一角;南美洲和北美洲相距遥远,而北美洲与欧亚大陆接近,有时相连。自新生代始,各陆块此升彼伏,不断分裂,缓慢漂移,相撞接合 ;逐渐演变成现代的海陆分布 。印度与亚洲连接发生于5000万年前的始新世;喜马拉雅山耸起则是200~300万年前的事,大致与此同时欧洲升起了阿尔卑斯山,美洲升起了落基山。第三纪时,中国境内现代地貌的轮廓已基本形成。当时除台湾、喜马拉雅和东南沿海一带有海侵外,其他广大地区为陆地。第三纪后期,由于强烈的喜马拉雅运动,使喜马拉雅、台湾等海槽褶皱隆起,并伴有基性岩浆喷发和侵入活动。第四纪的地壳运动以升降运动为主。 早第三纪气候比白垩纪寒冷。晚始新世和渐新世时,南极大陆出现小型冰盖,到中新世中期南极大陆形成相当于现代冰盖的2/3。更新世初北半球出现格陵兰冰盖,其后200万年间曾出现多次冰期和间冰期,总称为第四纪大冰期。 |
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条