1) Boundary layer


边界层
1.
Prediction of evaporation rate of mono-component liquid based on boundary layer theory of laminar flow;
基于层流边界层理论的单组分液体蒸发速率的预测
2.
Influence of boundary layers upon filtration law in low-permeability oil reservoirs;


低渗透储层原油边界层对渗流规律的影响
3.
Primary study on application of brilliant blue dye to indicating the boundary layer of solute transport;
应用亮兰染色剂指示溶质迁移边界层的研究
2) boundary layers


边界层
1.
A dissipation integral method is developed for calcalating compressible turbulentboundary layers on planar bodies.
发展了二维可压湍流边界层的耗散积分方法。
2.
In recent years, there have been some meaningful results onboundary layers of the incompressible Navier-Stokes equations, but there is few workon the compressible boundary layers.
边界层问题在物理、力学和工程等实际领域中是十分重要的。
3) planetary boundary layer


边界层
1.
A lidar system for monitoring planetary boundary layer aerosol in daytime;


激光雷达白天探测大气边界层气溶胶
2.
These analyses were based on the observation of the large\|scale rain sample and the correlative particles in 1993 in Qingdao region, as well as the monitoring of the large-scale meteorological conditions of the planetary boundary layer.
对 1993年青岛地区较大规模的雨样及相关粒种的观测 ,并配合大范围边界层污染气象的探测 ,对青岛地区酸雨的时空分布及酸雨的形成原因作了详细分析 。
3.
By using the radiosonde data in Sichuan Province and Chongqing Municipality during the June-August of 1998, the relationship between wind field in planetary boundary layer (PBL) at the eastern edge of the Tibetan Plateau and heavy rain-flood of the Changjiang River are analyzed.
应用1998年6~8月四川省和重庆市探空资料,分析了青藏高原东侧大气边界层风场演变与长江上游暴雨和长江洪水的关系。
4) PBL


边界层
1.
Modeling Study on the Land Surface Fluxes and the Structure of Planetary Boundary Layer(PBL) over Inner Mongolia Grassland;
内蒙古草原陆面通量和边界层结构数值模拟
2.
Research on the Sensitivity of Rainstorm Simulation to the PBL Parameterizations over the Yangtzi River Basin;
长江流域一次暴雨过程的模拟对行星边界层参数化的敏感性研究
3.
ON THE EXTENSION OF THE RESISTANCE LAW FOR PBL TO NON STATIONARY AND INHOMOGENEOUS CONDITIONS;
关于边界层阻力定律在非定常均匀条件下的推广
5) boundary layer edge


边界层边缘
6) temperature boundary layer


热边界层
1.
People are not completely aware of the importance in making use of the temperature boundary layer to reduce the resistance of the pipeline.
人们还没有完全认识到利用热边界层进行减阻的重要意义。
2.
In details, the reducing resistance theory and its application of temperature boundary layer in pipeline are studied in the paper.
全面研究了高粘性液体管道流动的热边界层减阻理论的应用。
3.
Wholly the theory of temperature boundary layer in pipeline is studied by the paper.


研究了高粘性液体管道流动的热边界层理论。
补充资料:边界层
| 边界层 boundary layer 高雷诺数绕流中紧贴物面的粘性力不可忽略的流动薄层。又称附面层。德国物理学家L.普朗特于1904年首先提出了边界层的概念。从那时起,边界层研究就成为流体力学中的一个重要课题和领域。在边界层内,紧贴物面的流体由于分子引力的作用 ,完全粘附于物面上 ,与物体的相对速度为零。由物面向外,流体速度迅速增大至当地自由流速度,即对应于理想绕流的速度,一般与来流速度同量级。因而速度的法向垂直表面的方向梯度很大,即使流体粘度不大,如空气、水等,粘性力相对于惯性力仍然很大,起着显著作用,因而属粘性流动。而在边界层外,速度梯度很小,粘性力可以忽略,流动可视为无粘或理想流动。在高雷诺数下,边界层很薄,其厚度远小于沿流动方向的长度,根据尺度和速度变化率的量级比较,可将纳维-斯托克斯方程简化为边界层方程。求解高雷诺数绕流问题时,可把流动分为边界层内的粘性流动和边界层外的理想流动两部分,分别迭代求解。边界层有层流、湍流、混合流 ,低速(不可压缩)、高速(可压缩)以及二维、三维之分。由于粘性与热传导紧密相关,高速流动中除速度边界层外,还有温度边界层。 边界层转捩 边界层中的流态由层流过渡为湍流的过程。转捩是一个十分复杂的流动变化过程,工程上常把转捩过程简化为一个突变现象。影响转捩的主要因素是雷诺数,若边界层当地雷诺数达到某一临界值时,即发生转捩。转捩还受其他许多因素影响,如外流的原始湍流度、逆压、梯度、流过曲面时离心力的作用、物面粗糙度、噪声、系统的稳定性以及流体与物体间的热交换等。 边界层厚度 边界层内从物面 (当地速度为零)开始,沿法线方向至速度与当地自由流速度U 相等(严格地说是等于0.990或0.995U)的位置之间的距离,记为 δ 。由绕流物体头部(前缘)起,边界层厚度从零开始沿流动方向逐渐增厚。以直匀流平行流过平板为例,层流和湍流边界层的厚度分别为 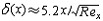 和 和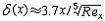 ,其中 Rex =Ux/v 为当地雷诺数,x为从前缘开始的流向距离 ,ν 为运动粘度。显然湍流边界层的厚度比层流发展得快。实用中又定义了边界层位移厚度δ*和动量损失厚度θ。对于不可压缩流动, ,其中 Rex =Ux/v 为当地雷诺数,x为从前缘开始的流向距离 ,ν 为运动粘度。显然湍流边界层的厚度比层流发展得快。实用中又定义了边界层位移厚度δ*和动量损失厚度θ。对于不可压缩流动,
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条
|
|
| ©2011 dictall.com | |