1) seismic wave


地震波
1.
Determination of water irruption feeder by using anisotropy of seismic wave;


用地震波的各向异性确定矿井突水通道的研究
2.
Sectional-decomposition numerical modeling of seismic wave field;


区域分解地震波场数值模拟算法
3.
Study on the influences of various seismic waves on response of bridge pier;


不同的地震波对桥墩地震反应的影响研究
2) earthquake wave


地震波
1.
Effect of earthquake wave frequency on dynamic response of tunnel;


地震波频率对巷道围岩动力响应的影响
2.
Study on influences of complicated site conditions on earthquake wave;


复杂场地条件对地震波影响研究综述
3.
On selection of earthquake wave for time history analysis;


时程分析用地震波选取的探讨
3) seismic waves


地震波
1.
Analysis on the dynamic response of the complex structure caused by different seismic waves;
复杂结构在不同地震波作用下的动力响应
2.
Based on the analyses of both statistics and frequency, it is found that the attenuation of seismic waves in the near region away from the explosion source is more abrupt than that in the middle and far regions; the vibration velocities of rock particles in the near region given by the Sodev抯 empirical formula are much greater than their practical values; the propagation of .
通过6次现场岩体爆破试验,测量出与爆源不等距离处的36组地震波形。
3.
In this paper,a semi-analytical method to calculate the response of pile groups embedded in a layered soil to arbitrary incident seismic waves is presented.
本文舍弃桩基动力分析中的土介质平面应变假定,采用薄层内位移线性变化条件下的动力Green函数形成桩-土-桩动力相互作用所需的土介质柔度矩阵,用梁单元模拟桩的运动,以地震波入射为初始运动输入,建立了适用于群桩基础对任意入射地震波响应的半解析分析模型,研究了层状土介质中群桩对不同角度入射SH、SV和P波的动力响应。
4) earthquake ground motion


地震波
1.
The Problems of estimating the time-varying spectrum of earthquake ground motions estimation using STFT, Wigner-Ville distribution, continuous wavelet transform, S-transform and improved S-transform with a complex window are addressed.
利用短时傅里叶变换(STFT)、Wigner-Ville分布、连续小波变换、S变换以及变复窗口的S变换等现代时频分析技术对地震波进行时变谱估计。
2.
The distinctive feature and status in quo of artificial ground motions is analyzed in this paper, which set forth a simplified method to describe the non stationary frequencies of earthquake ground motions and statistical laws.
分析了人造地震波的特点与现状 ,给出了地震动频率非平稳特性的简化描述方法与统计规律 ,采用 ARMA模型研究了拟合反应谱的人造地震波合成方法 ,并通过算例对该方法进行了验证。
5) earthquake waves


地震波
1.
Design method for subsea spools against earthquake waves;


地震波作用下海底管线弯管抗震设计方法
2.
The dynamic responses of the slurry wall subjected to earthquake waves;


在地震波作用下地下连续墙的动力响应
3.
Selection of earthquake waves and values of damping ratio for space structures in aseismic analysis;
空间结构抗震分析中的地震波选取与阻尼比取值
补充资料:地震波
| 地震波 seismic wave 由地震震源发出的在地球介质中传播的弹性波。地震发生时,震源区的介质发生急速的破裂和运动,这种扰动构成一个波源。由于地球介质的连续性,这种波动就向地球内部及表层各处传播开去,形成了连续介质中的弹性波。 地球介质,包括表层的岩石和地球深部物质,都不是完全弹性体,但因地球内部有很高的压力,地震波的传播速度很大,波动给介质带来的应力和应变是瞬时的,能量的消耗很小,因此可以近似地把地震波看作弹性波。 从震源发出的波动有两种成分: 一种代表介质体积的涨缩,称为涨缩波,其质点振动方向与传播方向一致,所以又称纵波。另一种成分代表介质的变形,称为畸变波,其质点振动方向与传播方向垂直,所以又称横波。纵波的传播速度较快,在远离震源的地方这两种波动就分开,纵波先到,横波次之。因此纵波又称P波,横波又称S波。在没有边界的均匀无限介质中,只能有P波和S波存在,它们可以在三维空间中向任何方向传播,所以叫做体波。但地球是有限的,有边界的。在界面附近,体波衍生出另一种形式的波,它们只能沿着界面传播,只要离开界面即很快衰减,这种波称为面波。面波有许多类型,它们的传播速度比体波慢,因此常比体波晚到,但振幅往往很大,振动周期较长。如果地震的震源较深,震级较小,则面波就不太发育。 波速随频率或波长而变化,这种现象叫做频散。在完全弹性的平行层介质中,由于各种类型的波的叠加,在地表观察到的面波频散是几何原因造成的。在地球内部,由于介质的不均匀性和非完全弹性,会导致体波的频散,这是物理原因造成的。由于频散,波形在传播过程中会发生变化。例如在震源处发出的一个脉冲,在远处就可以散成一个波列。 将地球介质看成完全弹性体只是一种近似。精密的观测表明,地震波在传播中的能量消耗有时是不能忽略的。在一定观测点,波的振幅A随时间t衰减可用A=Aoe-rx表示,r为时间衰减系数,Ao 为初始振幅。波传播x 距离后,因能量损耗而导致振幅的减小,可用 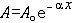 表示,a 为距离衰减系数。表示能量消耗的另一个重要参数Q称为品质因子,其定义是 表示,a 为距离衰减系数。表示能量消耗的另一个重要参数Q称为品质因子,其定义是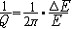
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条
|
|
| ©2011 dictall.com | |