1) small nitrogenous fertilizer


小氮肥
1.
Based on the technological features of small nitrogenous fertilizer production system and the analysis of fire & explosion risk factors in the production of nitrogenous fertilizer,Dow method is used to calculate the inherent risk index and the actual risk index of six assessment units of coal gas producer,gas tank,desulfurization,transformation,cuprammonium washing and synthesis.
结合小氮肥生产工艺的特点及企业实际情况,在分析小氮肥生产过程中火灾爆炸危险因素的基础上,应用道化学法对小氮肥生产工艺中的煤气发生炉、煤气柜、脱硫、变换、铜洗和合成等6个单元进行了固有危险指数和安全补偿措施后的危险指数的计算,同时对评价单元的火灾爆炸危险度进行了研讨。
2) small-scale nitrogenous fertilizer


小氮肥
1.
This article describes the popularization of eight high & new technologies in small-scale nitrogenous fertilizer industry.
将小氮肥行业尿素生产 8项高新技术向全行业推广。
3) small nitrogenous fertilizer factory


小氮肥厂
1.
This paper stated the reason and harm of producing waste gas,the way of dealing with and effects in small nitrogenous fertilizer factory.
阐述了小氮肥厂废气产生的原因与危害及其处理的方法与效
5) slag of gas generation in small-nitrogen fertilizer plant


小氮肥造气炉渣
6) N fertilizer


氮肥
1.
The border effect and utilization rate of N fertilizer as base under wheat intercropped with spinach;
小麦间作菠菜的边际效应与基施氮肥利用率
2.
Four treatments were designed as the control (without urea incorporation); low N fertilizer level(0.
鉴于氮肥施用对农田CH4排放的影响还有很大不确定性,室外盆栽试验于2 0 0 2年在南京农业大学实施。
3.
In this paper,the concept related to ~(15)N application were introduced and interpreted,and the studies on N fertilizer research,N cycling and agricultural environment protection since 1980 were reviewed in detail.
本文介绍了15N的相关概念,列举了20世纪80年代以来15N在氮肥研究、氮素转化研究以及农业环境保护中的应用进展,阐明了应用15N的新技术已解决的问题,以及将要解决的问题,并展望了性核素示踪技术的应用前景。
补充资料:氮肥
| 氮肥 nitrogen fertilizer 具有氮( N)标明量的单元肥料。施于土壤或植物可提高植物的氮营养水平。按氮的化学形态可分为三大类:①铵态氮肥 ,氮以 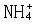 形态存在。主要有氨水 、液氨、碳酸氢铵、硫铵、氯化铵等。②硝态氮肥,氮以 形态存在。主要有氨水 、液氨、碳酸氢铵、硫铵、氯化铵等。②硝态氮肥,氮以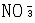 形态存在。主要有智利硝石(硝酸钠)、硝酸钙;同时含有 形态存在。主要有智利硝石(硝酸钠)、硝酸钙;同时含有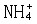 和 和 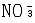 的氮肥有硝酸铵、硫硝酸铵、硝酸铵钙等。③酰胺态氮肥,氮以酰胺基形态存在。主要有尿素等。中国常用的氮肥有尿素、氨水、碳酸氢铵、硝酸铵、硫铵、氯化铵和含氮复合肥料。 的氮肥有硝酸铵、硫硝酸铵、硝酸铵钙等。③酰胺态氮肥,氮以酰胺基形态存在。主要有尿素等。中国常用的氮肥有尿素、氨水、碳酸氢铵、硝酸铵、硫铵、氯化铵和含氮复合肥料。氮肥施入土壤后,其中的氮素被当季植物吸收,一部分通过微生物的同化和粘粒矿物的固定等作用而残留在土壤中;还有一部分则通过各种途径,如氨的挥发、反硝化作用、淋洗作用和径流等离开土壤 -植物系统而损失掉 。土壤氮素含量、形态及其转化和供氮能力与氮肥肥效关系极大。土壤中氮分为无机态和有机态 2类 。无机态氮中,粘土矿物固定态的铵约占土壤全氮量的 2% ~ 3%,能被植物直接吸收利用,称有效态氮。有机态氮约占土壤表土全氮量的 90%或更高,经微生物分解转化为铵态氮和硝态氮后,易为作物吸收。 |
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条