1) Atomic emission spectrometry


原子发射光谱法
1.
An analytical method to determine trace elements in titanium white powder by atomic emission spectrometry was introduced in the paper.
研究了原子发射光谱法测定钛白粉中的杂质元素的分析方法。
2.
Using microwave plasma torch(MPT)as excitation light source, argon as support gas, the sample solution was introduced into a pneumatic atomizer system, and the method of determining copper, chromium, manganese and aluminum in hydrogenation catalyst by microwave plasma torch atomic emission spectrometry (MPT-AES) was studied.
用微波等离子体炬(MPT)为激发光源,氩气为等离子体工作气体,用气动雾化进样,研究了微波等离子体炬原子发射光谱法(MPT-AES)测定加氢催化剂中的Cu、Cr、Mn、Al四种金属元素的方法。
3.
Atomic emission spectrometry with spark discharge excitation was applied to the analysis of samples of stainless steel wires with diameter smaller than 8 mm.
火花激发原子发射光谱法应用于直径小于8 mm的不锈钢线材的分析,对此类试样应用了一种特制的夹具,用块状标准样品制作工作曲线。
2) AES


原子发射光谱法
1.
Evaluation of Microwave Plasma Torch in Determination of Mercury by AES;


微波等离子体炬原子发射光谱法测汞的评价
2.
Direct Determination of 15 Trace Impurities in Coke by AES


原子发射光谱法直接测定焦炭中的15种微量杂质元素
3.
A method for determination of acid soluble and full aluminium in low and medium alloy steel by AES was presented.
本文利用原子发射光谱法定量测定中低合金钢中的酸溶铝和全铝。
3) atomic emission spectroscopy


原子发射光谱法
1.
The method for determination is atomic emission spectroscopy、atomic absorption spectroscopy and differential absorptive stripping voltammeter.
对造纸工业常用的 1 0种植物原料 ,采用原子发射光谱法、原子吸收分光光度法和微分脉冲吸附溶出伏安法 ( DPS) ,对其中的金属离子含量进行了研究。
4) Double line of atomic emission spectroscopy


原子发射光谱双谱线法
5) spark source atomic emission spectrometry


火花源原子发射光谱法
1.
Determination of 14 impurity elements in pure gold by spark source atomic emission spectrometry;
火花源原子发射光谱法测定纯金中14种杂质元素
2.
Uncertainty in measurement and its evaluation in analysis and testing Part 4 Example(6):Evaluation of the uncertainty for measurement of molybdenum content in steel by spark source atomic emission spectrometry;
分析测试中测量不确定度及评定 第四部分 实例(6):火花源原子发射光谱法测定钢中钼量的不确定度评定
3.
Evaluation of uncertainty for measurement of carbon in titanium alloy by spark source atomic emission spectrometry;
火花源原子发射光谱法测定钛合金中碳的不确定度评定
6) flame atomic emission spectrometry


火焰原子发射光谱法
1.
Direct determination of sodium in surfactant of sodium salt by flame atomic emission spectrometry;
火焰原子发射光谱法直接测定钠盐表面活性剂中钠
2.
Direct Determination of Strontium in Mineral Water by Flame Atomic Emission Spectrometry;
火焰原子发射光谱法直接测定矿泉水中锶
3.
A method for the determination of microamount of sodium in titanium carbide samples by flame atomic emission spectrometry is reported in this paper.
对火焰原子发射光谱法测定碳化钛中微量钠的条件进行了试验。
补充资料:原子发射光谱法
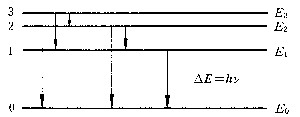
| 原子发射光谱法 atomic emission spectrometry 利用原子或离子在一定条件下受激而发射的特征光谱来研究物质化学组成的分析方法。根据激发机理不同,原子发射光谱有3种类型:① 原子的核外光学电子在受热能和电能激发而发射的光谱,通常所称的原子发射光谱法是指以电弧、电火花和电火焰( 如ICP等)为激发光源来得到原子光谱的分析方法。以化学火焰为激发光源来得到原子发射光谱的 ,专称为火焰光度法。②原子核外光学电子受到光能激发而发射的光谱,称为原子荧光(见原子荧光光谱分析)。③原子受到X射线光子或其他微观粒子激发使内层电子电离而出现空穴,较外层的电子跃迁到空穴 ,同时产生次级X射线即X射线荧光(见X射线荧光光谱分析)。 在通常的情况下,原子处于基态。基态原子受到激发跃迁到能量较高的激发态。激发态原子是不稳定的,平均寿命为10-10~10-8秒。随后激发原子就要跃迁回到低能态或基态,同时释放出多余的能量,如果以辐射的形式释放能量,该能量就是释放光子的能量。因为原子核外电子能量是量子化的,因此伴随电子跃迁而释放的光子能量就等于电子发生跃迁的两能级的能量差 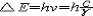 ,式中h为普朗克常数;c为光速;ν和λ分别为发射谱线的特征频率和特征波长。 ,式中h为普朗克常数;c为光速;ν和λ分别为发射谱线的特征频率和特征波长。
根据谱线的特征频率和特征波长可以进行定性分析。常用的光谱定性分析方法有铁光谱比较法和标准试样光谱比较法。 原子发射光谱的谱线强度I与试样中被测组分的浓度c成正比。据此可以进行光谱定量分析。光谱定量分析所依据的基本关系式是I=acb,式中b是自吸收系数,α为比例系数。为了补偿因实验条件波动而引起的谱线强度变化,通常用分析线和内标线强度比对元素含量的关系来进行光谱定量分析,称为内标法。常用的定量分析方法是标准曲线法和标准加入法。 原子发射光谱分析的优点是:①灵敏度高。许多元素绝对灵敏度为10-11~10-13克。②选择性好。许多化学性质相近而用化学方法难以分别测定的元素如铌和钽、锆和铪、稀土元素,其光谱性质有较大差异,用原子发射光谱法则容易进行各元素的单独测定。③分析速度快。可进行多元素同时测定。④试样消耗少(毫克级)。适用于微量样品和痕量无机物组分分析,广泛用于金属、矿石、合金、和各种材料的分析检验。 |
说明:补充资料仅用于学习参考,请勿用于其它任何用途。
参考词条